(Article courtesy of Wikipedia)
General Curtis sent the bulk of his 1st Division under Gen. James Blunt to confront the Confederates at Lexington, approximately forty miles east of Kansas City, on October 19. Blunt was unable to stop Price, but did slow his progress and gathered information on the Confederate forces. Again, at the Little Blue River on October 21, Blunt was forced to retire — but not without slowing Price enough for a pursuing Federal cavalry division under Alfred Pleasonton to close the gap between himself and the Rebels. Additional fighting occurred the next day at Independence, with Price emerging victorious yet again. Curtis was nearly sixty years old, and age had taken a toll on his desire for combat; however, thanks to his aggressive subordinate Gen. Blunt, Curtis decided to make another stand south of Westport. Blunt personally oversaw the construction of a defensive line south of the town along Brush Creek, perpendicular to the Kansas state line.
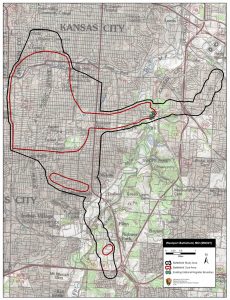
Map of Westport Battlefield core and study areas by the American Battlefield Protection Program
Price was aware of the forces to his front and rear, which together outnumbered him nearly three-to-one, so he determined to deal with them one at a time. He decided to attack Curtis’s army first, at Westport. Almost as old as his adversary, Price left direction of the engagement to his subordinate, General Jo Shelby. With about 500 wagons and 5,000 head of cattle, Price first needed a ford for his supply trains to cross the Blue River near Westport. One of Price’s divisions under John S. Marmaduke accordingly forced a crossing at Byram’s Ford on the 22nd, then took up positions on the west bank to hold off Pleasonton’s Federal Cavalry, which now threatened Price’s rear. Two other Confederate divisions, under Shelby and James Fagan, were poised to assault Blunt along Brush Creek the next day, hoping to defeat him before Pleasonton could arrive on the field in force.